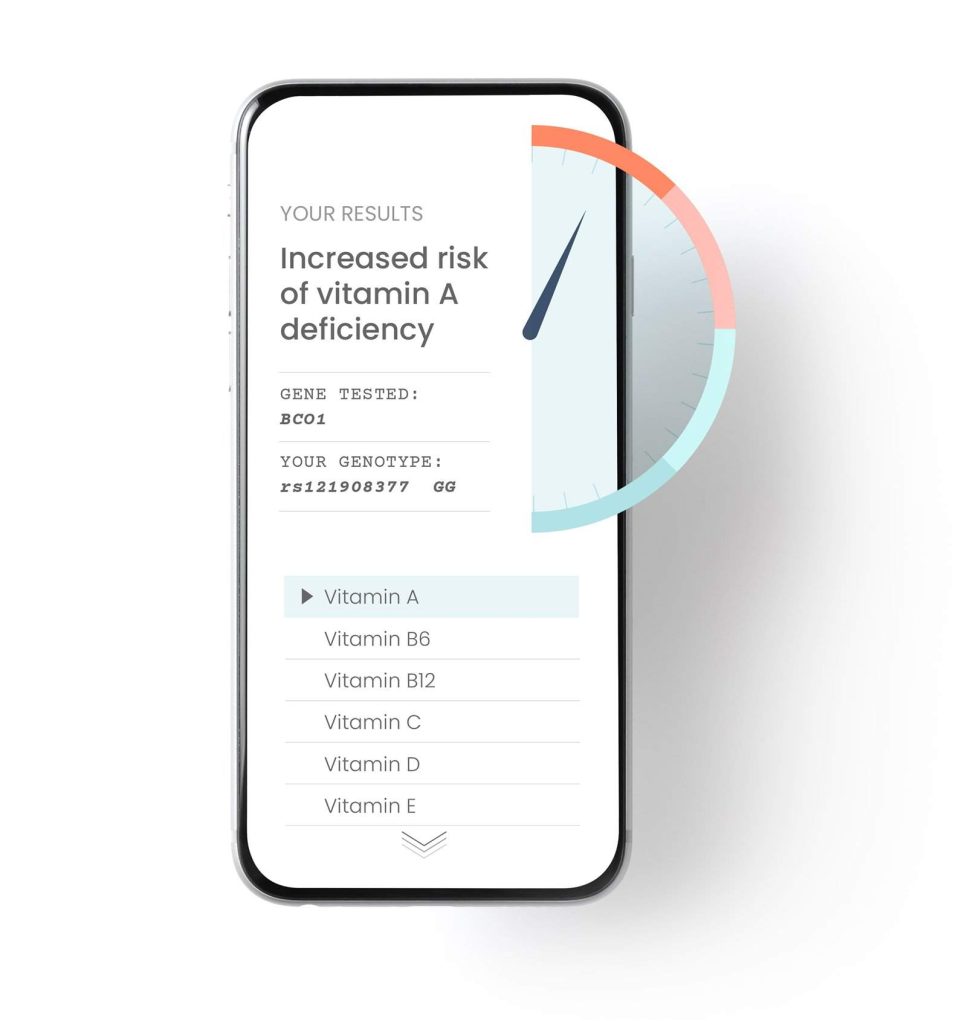
Cardiovascular Disease (ApoE) DNA Test
Find out if you have the APOE gene variant linked to cardiovascular disease.
The APOE gene influences both your risk of a heart attack, and your best approach to lower cholesterol levels. Find out your risk and the best treatment option for you.- Learn if you carry high-risk variants of the ApoE gene
- Discover your genetic predisposition for high cholesterol
- Optimize your heart health based on your DNA
฿15,200
AABB, ISO17025 & CLIA accredited lab
What is cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a group of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. The primary cause is often atherosclerosis – a fatty buildup inside blood vessels leading to plaque. This condition can:
- Limit blood flow, causing pain in areas like the arms and legs.
- Cause strokes if vessels in the brain are blocked.
- Result in heart attacks when the heart’s vessels are obstructed.
Other CVDs include heart failure (ineffective blood pumping), arrhythmia (uneven heartbeats), and stenosis (faulty heart valves).
What causes cardiovascular disease?
A key risk factor is high “bad” cholesterol (LDL-cholesterol) in the blood. This can lead to fatty buildup in vessels and plaque formation. Elevated LDL-cholesterol can come from:
- Genes like APOE, LDLR, APOB, and PCSK9.
- Lifestyle: Gender, age, excessive alcohol, fatty diets, little exercise, obesity.
- Conditions like Hyperlipoproteinemia type III, which affects cholesterol handling.
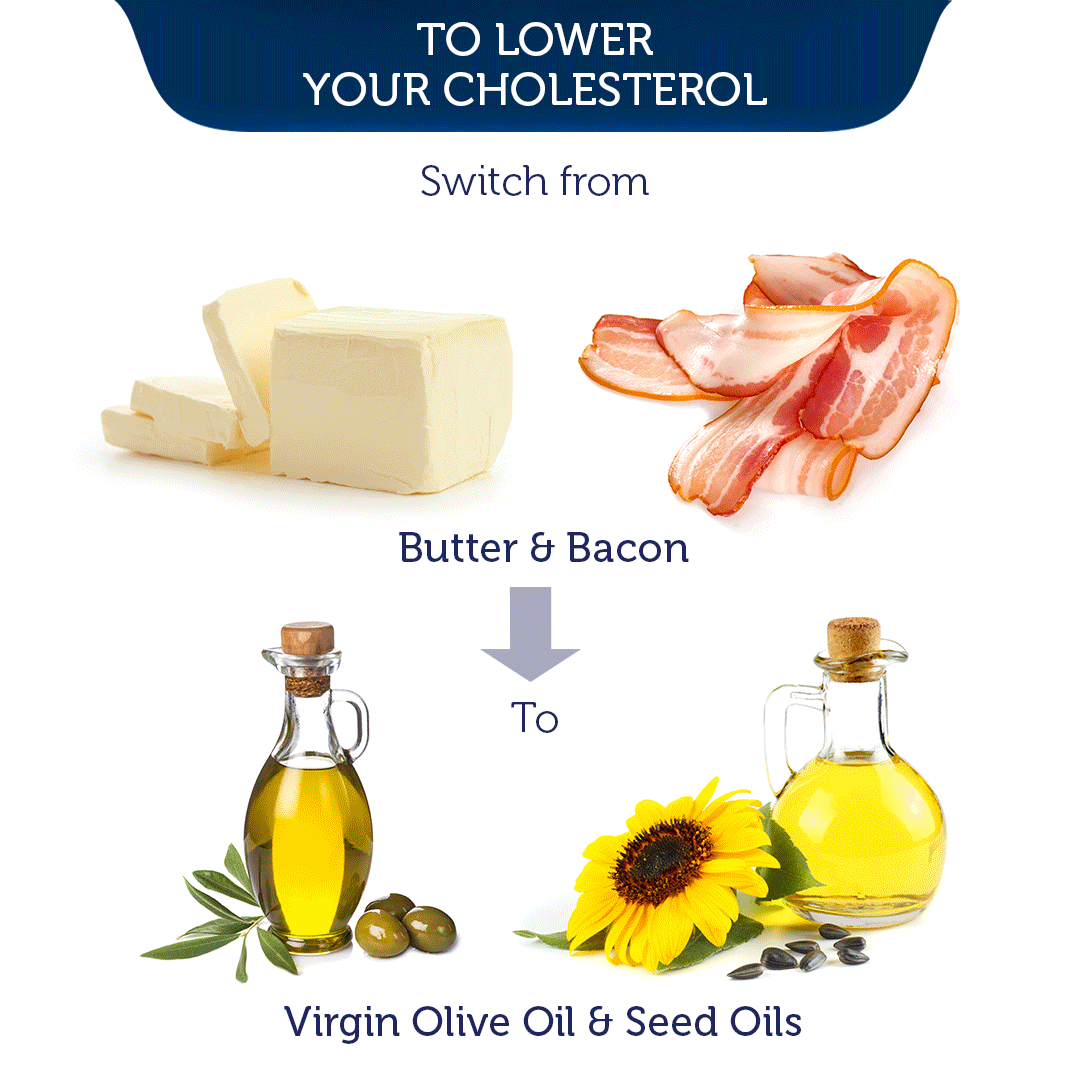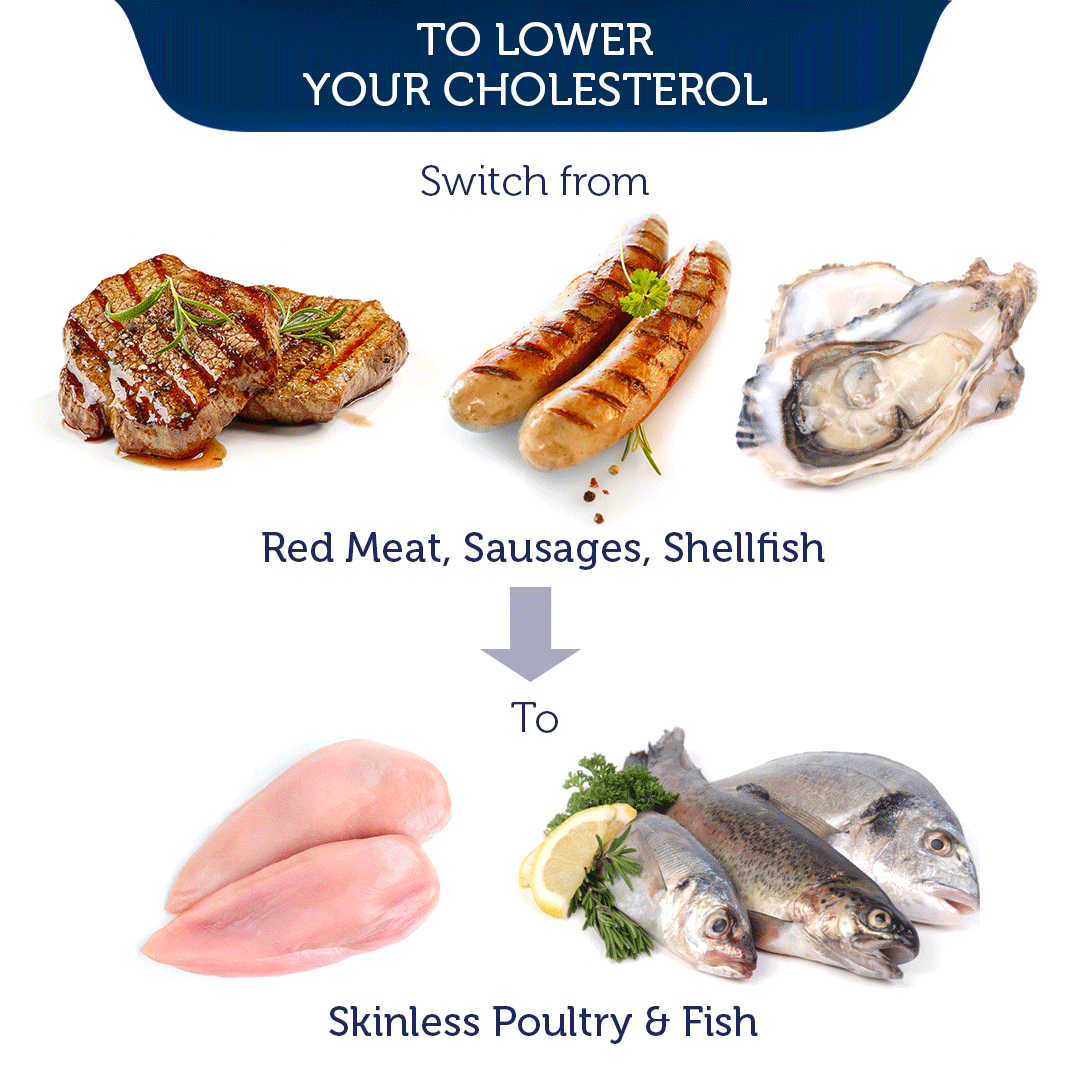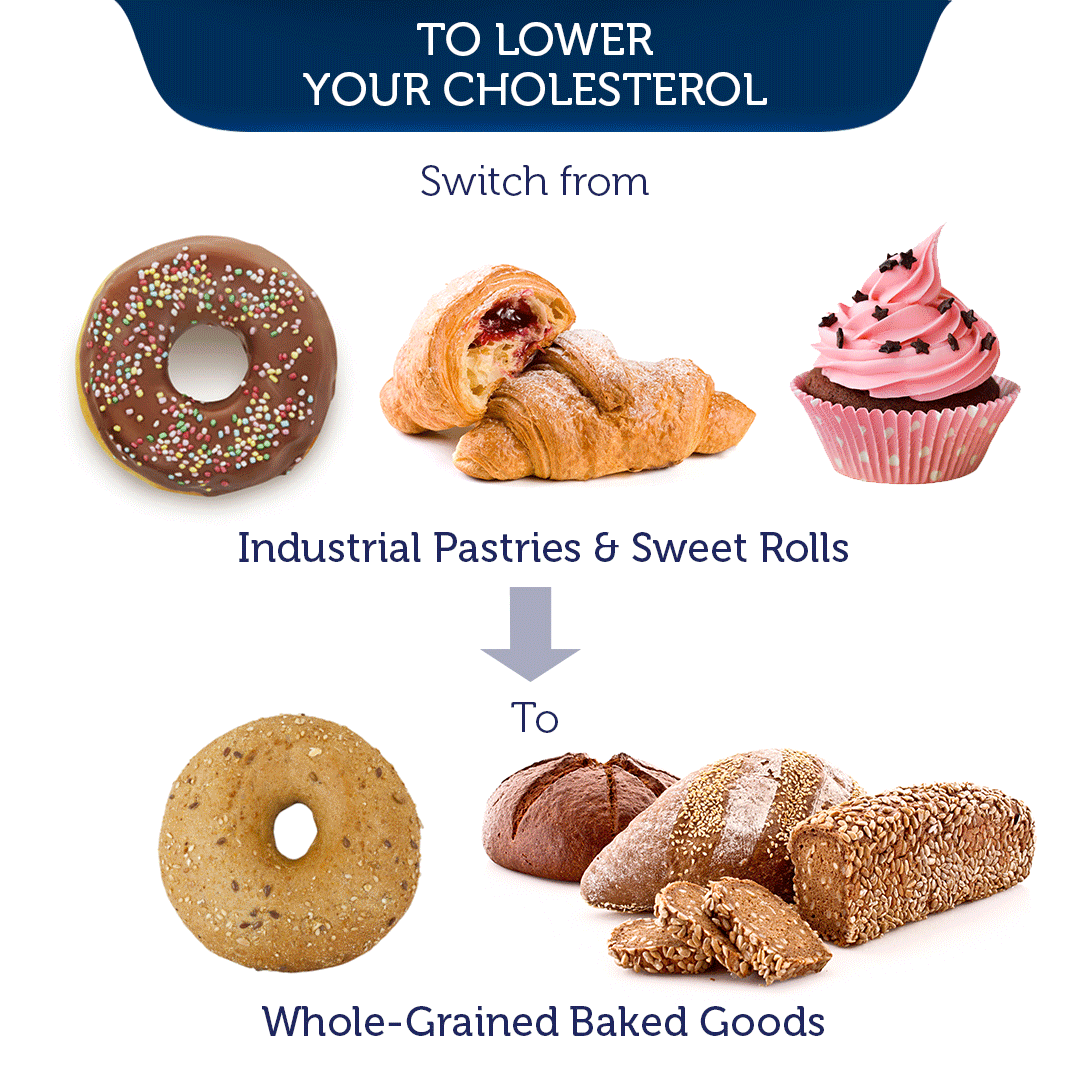
APOE DNA Testing and What It Means for You
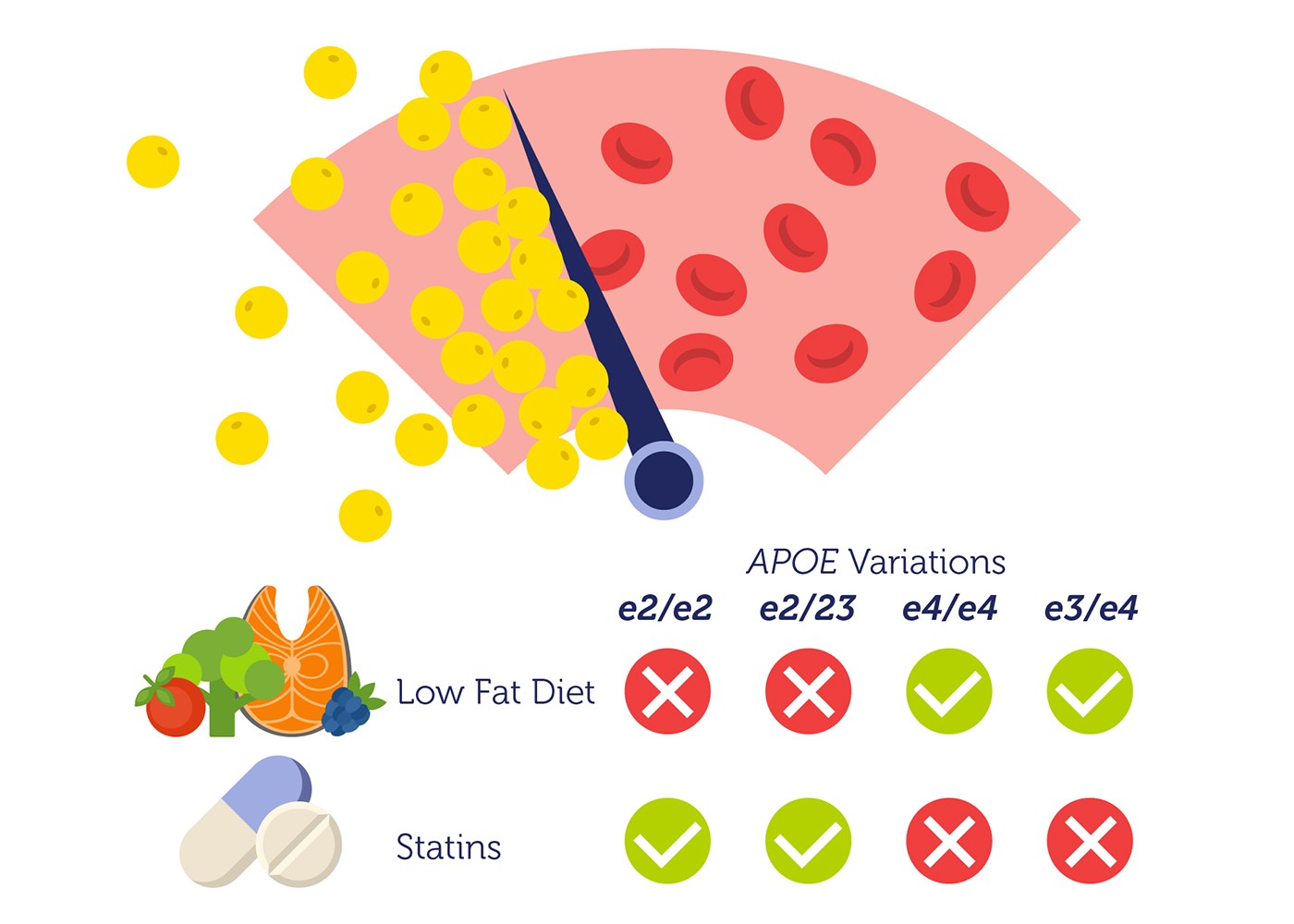
DNA testing can identify which APOE alleles you’ve inherited. With three possible alleles (e2, e3, e4), you can either inherit two identical alleles or two different ones. Here’s what each combination suggests:
- e2/e2: Linked to lower LDL-cholesterol levels but a higher risk of hyperlipoproteinemia type III. People with this combo typically respond well to statins.
- e2/e3 & e3/e3: These combinations don’t elevate the risk for high LDL-cholesterol. Individuals with either pairing tend to react positively to statins.
- e3/e4 & e4/e4: These pairs heighten the risk of cardiovascular diseases due to increased LDL-cholesterol. Statins aren’t typically effective for these individuals, but a low-fat diet can be beneficial.
- e2/e4: This lesser-known combination has mixed research findings. Some studies link it to a heightened LDL-cholesterol risk (because of the e4 allele), while others suggest a neutral risk similar to the e3/e3 pair.
How is APOE involved in cardiovascular disease?
The APOE gene helps regulate cholesterol. There are three common APOE versions (alleles): e2, e3, and e4.
- The e3 allele is the most common and neutral concerning CVD risk.
- The e4 allele increases the risk of high LDL-cholesterol and CVD.
- The e2 allele doesn’t raise LDL-cholesterol risk but does increase the risk for hyperlipoproteinemia type III for those with the e2/e2 genotype.
How do APOE genotypes respond to diet and statins?
Different APOE versions also affect response to diet and cholesterol drugs called statins. People with e3/e3 and e2/e3 genotypes often respond well to statins.
Those with e2/e2 also respond to statins but do better on low-sugar/carb diets. People at higher CVD risk from e3/e4 or e4/e4 genotypes respond poorly to statins. For them, a low-fat diet works better to lower LDL before CVD develops.
How Home DNA Testing Works

Order Test Kit
From relationship tests to health tests, we offer a wide range of DNA tests to fit your needs.

Collect & Ship
Collect your DNA with our painless mouth swabs, then send the samples to our laboratory for analysis

Receive Results
Access your confidential results online the moment testing is completed. Our team of experts is available for any questions.
Electronic Reports Delivery